Member-only story
The Invariant principle — Introduction and examples
Understand the famous mathematical property which acted as bane for several complex real life problems and still kicks a punch here and there.

Introduction
The dictionary defines ‘invariant’ as ‘never changing’, and well that’s really all there is. Invariant in mathematics, is a property held by a mathematical object, which remains same even after repetitive transformation of the object. If for some objects that property is different, then we can never reach from the original object to the newer ones, by trying the same transformations. This may sound tricky, but its really helpful and in some cases may even solve the problem.
Types
There are basically two broad categories,
- Invariance: Property that stays constants.
- Mono-variance: Property that changes in only one-direction. Its either always increasing or decreasing.
As Arthur Engel said it, “Invariance principle is a heuristic principle, its best learned by experience”, lets try to solve some examples to understand.
Example 1: Lone survivor
Statement: Suppose there are 1 to 1000 numbers written on a paper. At each step, we select any two numbers (randomly) and replace them with their difference. Is it possible to have 243 in the end as the only remaining number?
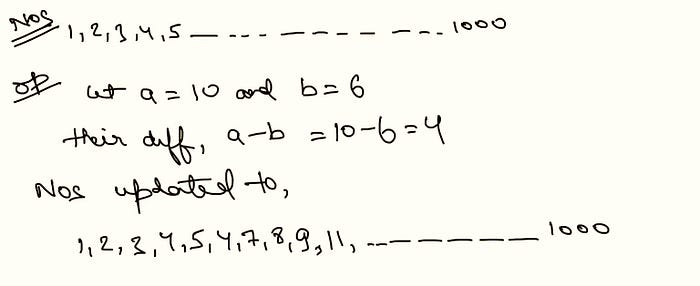
Inference: Well that’s good question to start with, and may get tricky for some. The brute force logic says to start with all the numbers and keep trying all the possible combinations of selecting 2 numbers out of 1000. Then do it again, and again and if you ever reach 243 in the end, the answer is ‘yes’ otherwise, ‘maybe’ as there are still many ways left to solve this. Enter invariance. (Note, try to find some property which is never changing as we perform the operation before going further)
Solution:
